I. Introduction: What Is Welding Hardware?
Welding hardware refers to the essential tools and accessories used to join metal parts through welding. These components—from clamps and electrodes to filler wires and protective gear—ensure welding works efficiently and safely. They play a key role in metal fabrication, construction, machinery repair, and many industrial tasks. This guide will walk you through the main types of welding hardware, common applications, and how to choose the right tools for your needs.
2. Common Types of Welding Hardware
Welding hardware includes everything from small hand tools used for electronic work to specialized machines used in industrial metal fabrication. Each category serves different needs and contributes to efficient, precise welding operations.
2.1 Handheld Welding Tools (Electronic Welding)
Handheld welding tools are commonly used for electronics, circuit boards, and precision hardware assembly. They allow technicians to perform small-scale, accurate soldering tasks.
2.1.1 Soldering Iron / Soldering Station
The core tool for manual soldering, a soldering iron melts solder to connect electronic components.

Common types include:
· Nickel-chromium heater irons – durable, simple structure, stable heating
· Ceramic heater irons – heat up quickly and offer precise temperature control, making temperature-adjustable soldering stations a popular choice among professionals
2.1.2 Soldering Iron Stand
Designed to safely hold the soldering iron when not in use, preventing accidental burns and protecting the tip from damage.
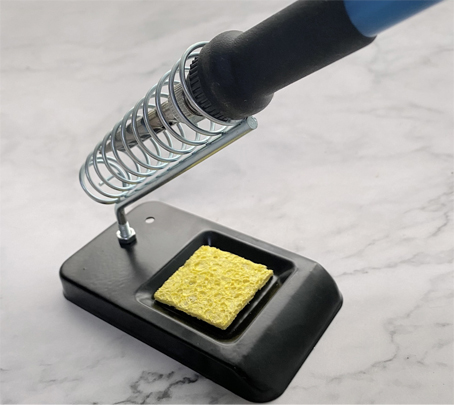

2.1.3 Soldering Tips
Available in various shapes such as pointed, beveled, and chisel tips. Each type suits different solder joint sizes and applications.

2.1.4 Hot Air Gun
Used to heat larger areas or remove components, especially SMD parts. Also useful for plastic welding and thermal shrink applications.

2.1.5 Tip Cleaner
Keeps soldering tips free of oxidation and improves heat transfer. Common options include brass wool and wet sponges.

2.1.6 Solder Paste / Flux
Improves solder flow, enhances wetting, prevents oxidation, and helps create stronger solder joints.

2.1.7 Desoldering Wick / Pump
Used to remove excess solder during repair or rework and to clean old solder joints.

2.1.8 Additional Tools
Tweezers, needle-nose pliers, diagonal cutters, wire strippers, magnifiers, and anti-static wristbands all help improve accuracy and safety during electronic soldering tasks.
2.2 Metal Welding Equipment (Industrial Welding)
2.2.1 Welding Machines
Welding machines are the core of metal welding operations, and different types are suited to different materials and working environments.
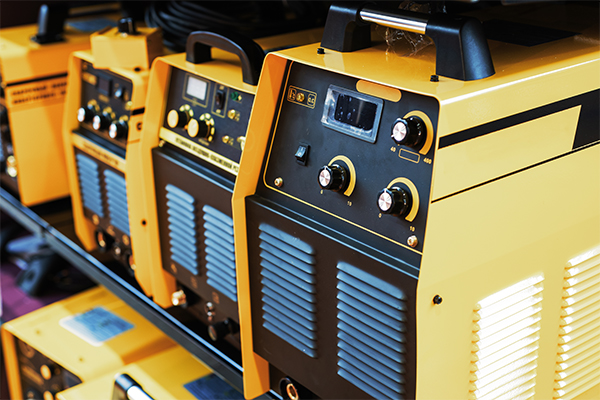

· AC/DC welders & SMAW stick welders – ideal for outdoor work, structural repairs, and heavy-duty joints
· MIG (CO₂) welders – versatile, easy to learn, and widely used in general metal fabrication
· TIG welders – preferred for aluminum, stainless steel, and high-precision work with clean, attractive welds
· Spot welders, butt welders, laser welders – designed for industrial production and high-strength structural welding
2.2.2 Electrode Holder
Used in stick welding to hold the welding rod and conduct current safely.

2.2.3 Slag Hammer
Used to knock off welding slag after each pass, ensuring a cleaner, more visible weld seam.

2.2.4 Electrode Oven / Storage Tube
Keeps electrodes dry and prevents porosity in the weld—especially important for low-hydrogen electrodes.

2.2.5 Angle Grinder
Used to remove rust, oxide layers, or burrs from metal surfaces before welding, as well as for weld finishing afterward.

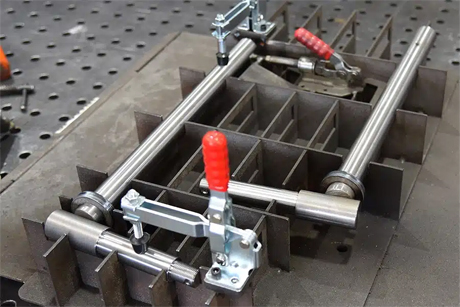
2.2.6 Welding Clamps & Fixtures
Secure the workpieces in the correct position, ensuring better angles, alignment, and overall welding accuracy.
3. How to Choose the Right Welding Hardware
Selecting welding hardware depends on the application, metal type, material thickness, and the precision required. The right choice directly improves efficiency, weld quality, and safety.
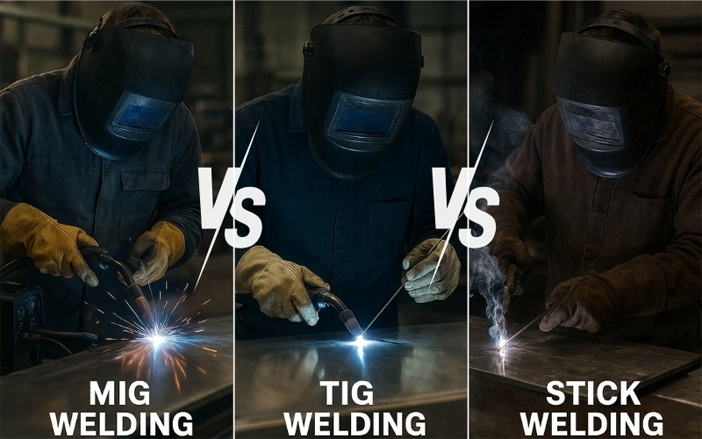

3.1 Choosing the Right Welder for the Job
Each welding task may require a different type of machine:
· General metal fabrication: MIG welders are fast, easy to use, and suitable for beginners and professionals.
· Outdoor repair or hard-to-reach areas: Stick welders (SMAW) work well in windy or unstable environments and tolerate dirty or rusty surfaces.
· Precision welding for thin materials or aluminum: TIG welders produce clean, controlled arcs with high-quality weld beads.
Regardless of the machine type, always consider output power, safety certifications, ease of use, and portability.
3.2 Choosing Welding Methods Based on Material Type
Different metals respond better to certain welding processes:
· Steel: MIG welding offers efficiency and strong weld penetration.
· Thick or structural metal: Stick welding provides deeper penetration and strong joints.
· Aluminum and thin sheet metal: TIG welding reduces burn-through and yields cleaner results.
Matching the welding process to the material’s characteristics is key to achieving optimal performance.
4. Safety Considerations During Welding
Welding involves high temperatures, sparks, and electrical hazards. Ensuring personal safety and a safe working environment is essential before starting any welding task.
4.1 Personal Protection
4.1.1 Wear Proper Gear
Use a welding helmet, safety goggles, heat-resistant gloves, fire-resistant sleeves, and insulated shoes.
4.1.2 Keep Your Body Dry
Avoid working in wet environments and never touch energized metal surfaces when sweaty or damp.
4.1.3 Wear Long-Sleeve Protective Clothing
This minimizes skin exposure and protects from sparks and molten metal.

4.2 Environmental Safety
4.2.1 Ensure Proper Ventilation
Use fume extractors or work in well-ventilated areas to prevent inhaling harmful fumes.
4.2.2 Keep Flammable Items Away
Remove any liquids or materials that could ignite, such as oil, alcohol, wood, or solvents.
4.2.3 Prepare Emergency Equipment
Fire extinguishers, sand buckets, and emergency spray cans should be readily accessible.
4.2.4 Restrict Access to the Welding Area
Use warning signs or temporary barriers to keep unauthorized personnel away.
4.2.5 Avoid Welding in Bad Weather
Stop outdoor welding during thunderstorms to prevent electrical accidents and equipment damage.
5. Conclusion
Welding hardware is fundamental in both industrial manufacturing and everyday repair. From handheld soldering tools to professional-grade welding machines, each piece of equipment plays a key role in connecting, assembling, or restoring metal components. Choosing the right welding hardware not only improves efficiency but also ensures durability and operational safety.
Whether you're a professional welder, a workshop operator, or a DIY enthusiast, understanding different welding tools and their applications can help you complete welding tasks more effectively and confidently.
