In today's era of rapid industrial progress, measuring tools are no longer just simple instruments for checking length or weight. With industries such as manufacturing, construction, and scientific research demanding greater accuracy and efficiency, the development of measuring instruments has taken a giant leap forward. Modern tools are smarter, more precise, and increasingly eco-friendly, thanks to innovations in materials and digital technology.
Below, let's explore the main types of measuring tools and their ongoing evolution.
1. Mechanical Measuring Tools
Traditional yet reliable, mechanical tools remain the foundation of measurement. Calipers, micrometers, dial indicators, and tape measures fall into this category.
· Features: Simple structure, low cost, and suitable for general measurement tasks. For example, high-quality tape measures now use embossed surfaces and strong alloy materials to resist wear, with accuracy reaching ±0.1mm in some models.
· Upgrades: Through the use of special alloys and precision machining, modern mechanical tools offer better durability and longer service life.

Mechanical measuring tools
 Tip: For basic measurement needs in workshops or construction sites, a mechanical toolset is still the most cost-effective option.
Tip: For basic measurement needs in workshops or construction sites, a mechanical toolset is still the most cost-effective option.
2. Electronic Measuring Tools
As industries move toward digitalization, electronic tools such as digital calipers, electronic scales, and laser distance meters are becoming mainstream.
· Features: High precision (e.g., laser distance meters with errors as low as ±1mm/10m), fast response, and built-in data storage. Many models include intelligent features like auto-calibration.
· Eco-friendly innovation: Use of low-power sensors and recyclable materials reduces electronic waste.
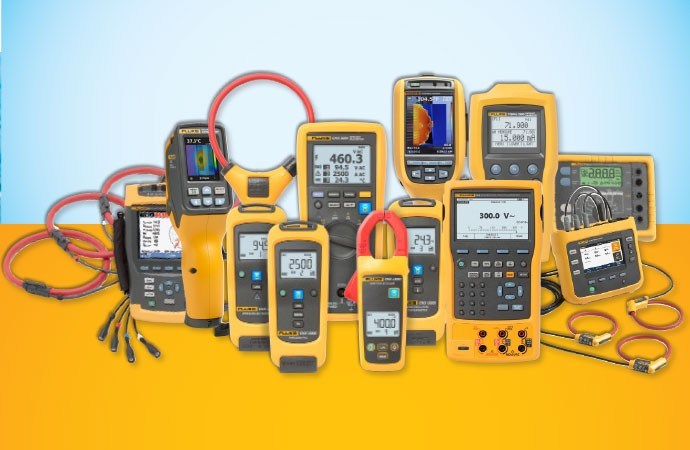

Electrical measuring instruments
3. Optical Measuring Tools
When contactless measurement is required, optical tools come into play. Instruments such as microscopes, projectors, and infrared thermal imagers are essential in precision manufacturing, especially in semiconductor inspection.
· Features: Non-contact measurement and extreme accuracy. Modern designs apply Mylar coatings and nanotechnology to enhance the stability of optical components, extending their lifespan by up to tenfold.
· Upgrades: With integrated AI image analysis, optical measuring tools can now deliver real-time data feedback, accelerating quality control.
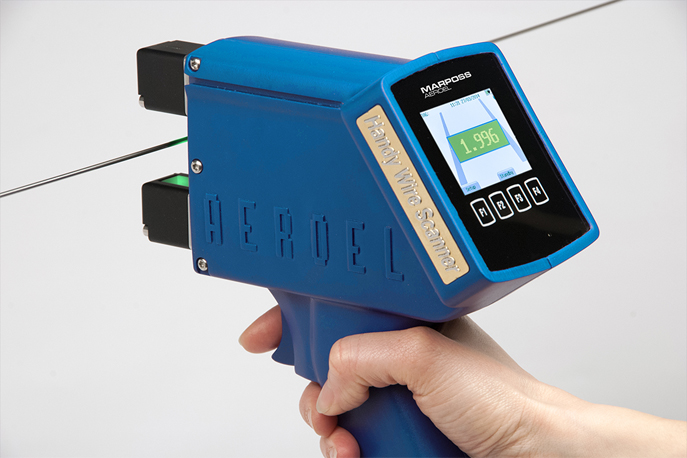

MARPOSS portable optical micrometer
4. Digital and Smart Measuring Tools
One of the fastest-growing categories is smart measuring tools, which integrate IoT and cloud computing. Examples include coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), smart tape measures with Bluetooth connectivity, and AR-based measurement systems.
· Features: Remote monitoring, big data analysis, and reduced human error. A Bluetooth-enabled smart tape measure can sync directly with an app to save data instantly.
· Eco-friendly design: Modular structures make it easier to upgrade components instead of replacing entire devices, reducing waste.
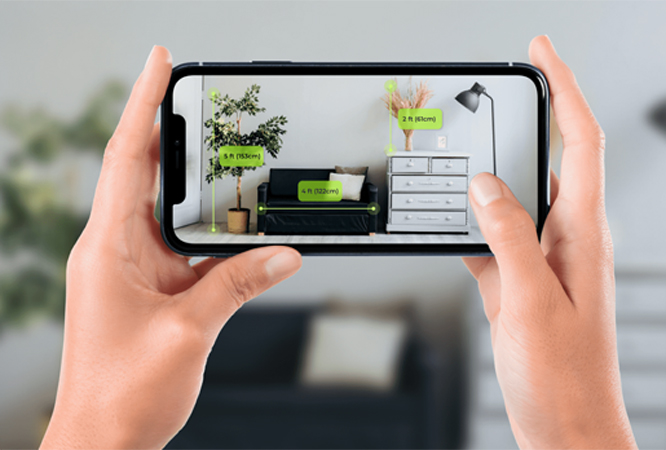

Image source: Augmented Reality Measurement App Development Guide for Product Owners
5. Multi-Functional Measuring Tools
Modern industries require versatility. That's why multi-functional tools, such as 3D laser scanners and integrated surveying devices, are gaining popularity.
· Features: One tool performs multiple functions—distance measurement, angle calculation, and even temperature detection. In construction, 3D scanners not only measure but also generate accurate 3D models, significantly shortening project timelines.
· Upgrades: Lightweight composite materials enhance portability without sacrificing strength.
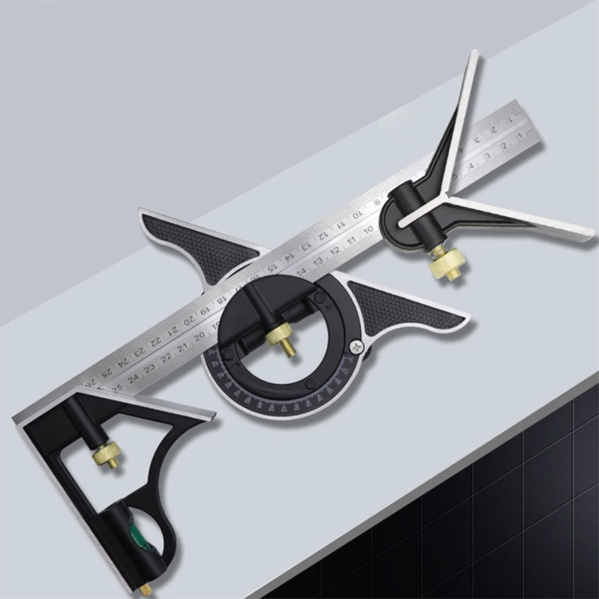
Multifunctional measuring ruler
Industry Trends at a Glance
· Material Innovation: High-strength alloys and ceramic composites boost both accuracy and durability.
· Smart Technology: AI and IoT accelerate the shift toward automation and remote operation.
· Sustainable Design: Energy-efficient sensors and recyclable materials align with modern green manufacturing goals.
 Tip: When choosing new measuring tools, consider not only precision but also whether the product supports future upgrades or integration with digital systems. This will extend its usability in the age of Industry 4.0.
Tip: When choosing new measuring tools, consider not only precision but also whether the product supports future upgrades or integration with digital systems. This will extend its usability in the age of Industry 4.0.
Conclusion
From mechanical calipers to AI-powered 3D scanners, measuring tools have evolved far beyond their traditional forms. The push toward higher precision, multi-functionality, and sustainability reflects the changing needs of modern industries. For suppliers and wholesale distributors, offering advanced solutions is no longer optional—it's essential.
As Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing continue to expand, the role of measuring tools will remain central, bridging the gap between innovation and precision.
