What Are Power Tools?
Power tools are mechanical devices driven by electric motors or electromagnets. Through a transmission mechanism, these tools convert electrical energy into mechanical motion to perform various tasks such as drilling, cutting, grinding, polishing, and fastening. Compared with traditional hand tools, power tools offer higher efficiency, greater precision, and reduced labor intensity — making them essential for construction, woodworking, metalworking, and home improvement projects.
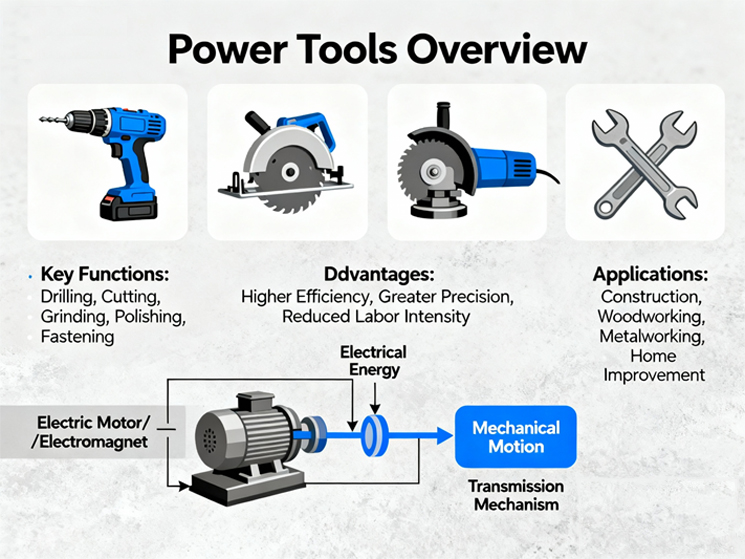
Main Categories of Power Tools
1. By Holding Method
Power tools can be divided into hand-held and portable (bench-type) types based on how they are operated.
· Hand-held Power Tools

These are lightweight, compact tools that can be operated directly by hand or suspended for use. Examples include electric drills, angle grinders, and impact wrenches. They are ideal for quick, flexible work and are widely used by technicians, DIY enthusiasts, and professional contractors.
· Portable or Bench-Type Power Tools

Portable tools are larger and more stable than hand-held ones. They must meet the following criteria:
a) Operated by one person
b) Can be moved when needed
c) Must be placed securely before use
d) Powered via a plug connection
e) Operate within a power limit (usually single-phase ≤2500W or three-phase ≤4000W).
2. By Application or Purpose
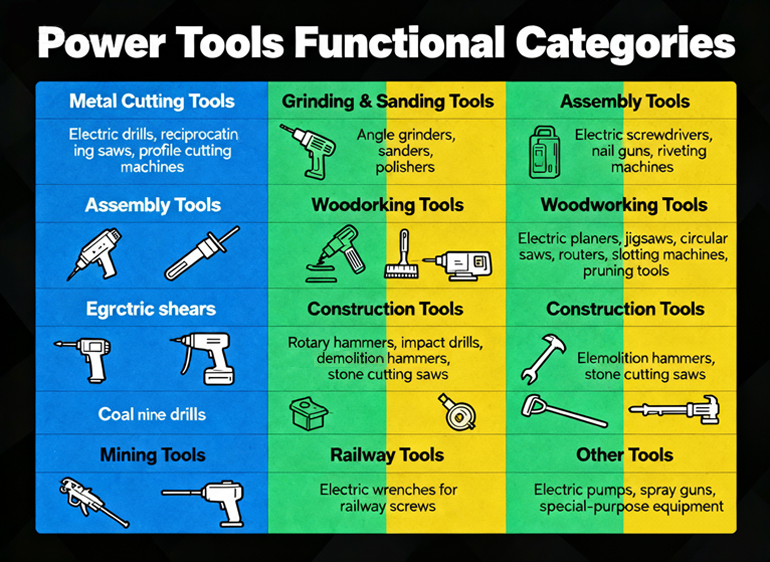
Power tools come in a wide range of functional categories designed for specific industries and materials:
· Metal Cutting Tools (J): Electric drills, reciprocating saws, and profile cutting machines for processing steel, aluminum, and other metals.
· Grinding & Sanding Tools (S): Angle grinders, sanders, and polishers for surface finishing and smoothness.
· Assembly Tools (P): Electric screwdrivers, nail guns, and riveting machines that improve fastening speed and accuracy.
· Woodworking Tools (M): Electric planers, jigsaws, circular saws, routers, slotting machines, and pruning tools used in furniture and carpentry work.
· Agricultural Tools (N): Electric shears for sheep and livestock maintenance.
· Construction Tools (Z): Rotary hammers, impact drills, demolition hammers, and stone cutting saws commonly used on building sites.
· Mining Tools (K): Coal mine drills designed for high endurance in underground conditions.
· Railway Tools (T): Electric wrenches used for tightening railway screws.
· Other Tools (Q): Electric pumps, spray guns, and other special-purpose equipment.
3. By Electrical Safety Classification

Electrical safety is a crucial factor when selecting power tools. They are generally classified into three protection levels:
· Class I Tools: Equipped with basic insulation and an additional grounding connection. The conductive parts are connected to the protective earth wire to prevent electric shock if insulation fails.
· Class II Tools: Protected by double or reinforced insulation, eliminating the need for grounding. These are safer and suitable for general indoor and outdoor environments.
· Class III Tools: Powered by safety extra-low voltage (SELV) — typically 24V or 42V — ensuring no hazardous voltage exists inside the tool. These are often used in high-risk or damp environments.
Choosing the Right Power Tool
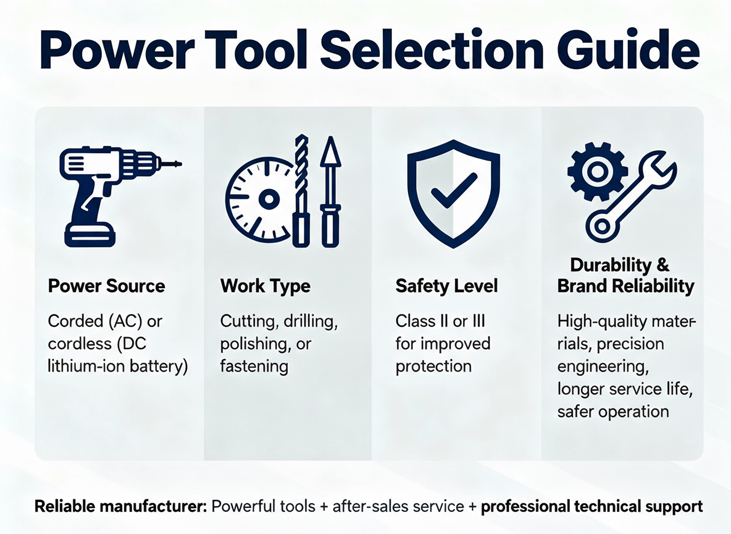
When selecting power tools, consider factors such as:
· Power Source: Corded (AC) or cordless (DC lithium-ion battery).
· Work Type: Cutting, drilling, polishing, or fastening.
· Safety Level: Choose Class II or III for improved protection.
· Durability and Brand Reliability: High-quality materials and precision engineering ensure longer service life and safer operation.
A reliable manufacturer provides not only powerful and efficient tools but also after-sales service and professional technical support.
Conclusion
Power tools have revolutionized the way professionals and hobbyists approach construction, metalwork, woodworking, and maintenance tasks. Understanding their types, functions, and safety standards helps you make informed choices and improve productivity. Whether you need a cordless drill, angle grinder, or impact wrench, investing in well-built, high-performance power tools ensures precision, safety, and long-term value.
